AndroPyTool
Update! DroidBox images were fixed. Dynamic analysis is working now.
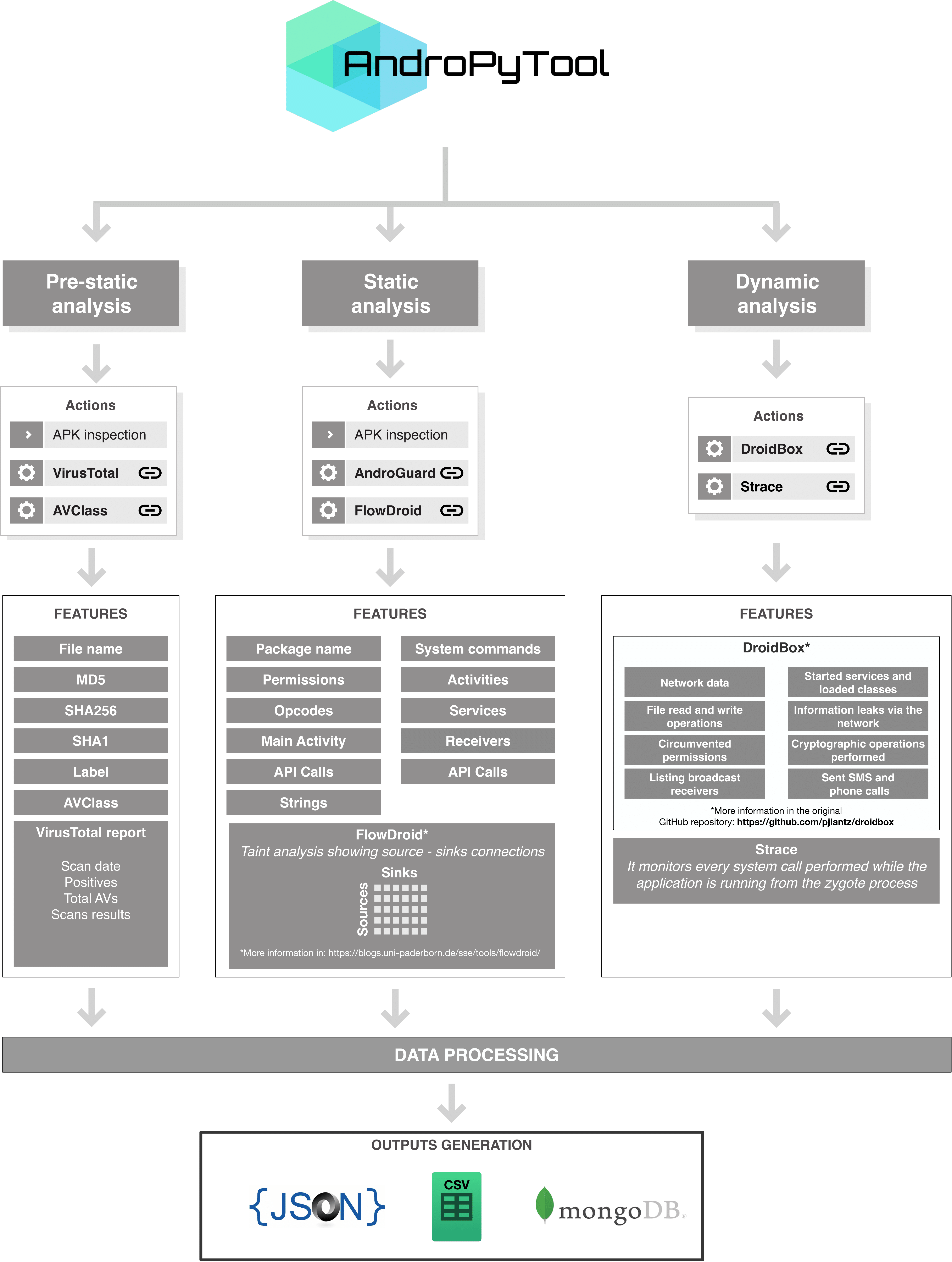
This is a tool for extracting static and dynamic features from Android APKs. It combines different well-known Android apps analysis tools such as DroidBox, FlowDroid, Strace, AndroGuard or VirusTotal analysis. Provided a source directory containing APK files, AndroPyTool applies all these tools to perform pre-static, static and dynamic analysis and generates files of features in JSON and CSV formats and also allows to save all the data in a MongoDB database.
To obtain more information you can read the following two papers:
-
Martín, A., Lara-Cabrera, R., & Camacho, D. (2018). Android malware detection through hybrid features fusion and ensemble classifiers: the AndroPyTool framework and the OmniDroid dataset. Information Fusion. DOI: 10.1016/j.inffus.2018.12.006
-
Martín, A., Lara-Cabrera, R., & Camacho, D. (2018). A new tool for static and dynamic Android malware analysis. In Data Science and Knowledge Engineering for Sensing Decision Support (pp. 509-516). World Scientific.
Please, if you use this tool, cite the above works in your papers.
How to install
There are two possible ways of installing and using AndroPyTool.
MODE A - DOCKER: Downloading a Docker container which contains all neccesary files. This is the recommended option, you can have AndroPyTool running in just two steps.
MODE B - SOURCE CODE: Installing and configuring all necessary libraries and running the Python source code.
MODE A - USING A DOCKER CONTAINER
A Docker container has been built in order to provide a fast and reliable version of AndroPyTool. To use AndroPyTool using Docker you just need to:
-
Install Docker (if you have not done so already). Follow the intructions here. If you are not using Ubuntu, change to the correct Operating System.
- Pull the container from Docker hub:
$ docker pull alexmyg/andropytool - Run AndroPyTool by launching the container:
$ docker run --volume=</PATH/TO/FOLDER/WITH/APKS/>:/apks alexmyg/andropytool -s /apks/ <ARGUMENTS>You need to replace </PATH/TO/FOLDER/WITH/APKS/> with a path of your host that contains the apks to be analysed. The argument “-s” must be provided as shown in the line above, pointing to /apks/
NOTE 2: AndroPyTool moves your APK files to different subfolder in order to generate an organised working directory. See the folders structure scheme.
There are different arguments that can be provided to androPyTool:
-h: Show the help message and exit.-all,--allsteps: Executes all steps of AndroPyTool (Recommended). In order to obtain a VirusTotal report, the argument -vt must be also provided followed by a VirusTotal API key. If the -all option is not provided, then only the last step is executed plus the provided arguments.-s SOURCE_FOLDER,--source SOURCE_FOLDER: Folder containing APKs to be analysed. All samples must include .apk extension. If a previous execution of AndroPyTool was interrupted, the previous working directory must me provided.-S,--single: Save single analysis separately. Default: False.-f,--filter: Filter valid and invalid APKs (Recommended).-vt VIRUSTOTAL_API_KEY,--virustotal VIRUSTOTAL_API_KEY: Analyse applications with the VirusTotal service. It must be followed by a VirusTotal API key.-cl,--classify: Classify apps between malware or benignware based on theVirusTotal reports. –virustotal argument has to be set-fw,--flowdroid: Run flowdroid.-dr,--droidbox: Run droidbox.-c,--cleanup: Perform cleanup deleting temporary working files. Default: True-P PACKAGEINDEX,--packgeIndex PACKAGEINDEX: TXT file with all Android API packages. Default: info/package_index.txt-C CLASSINDEX,--classIndex CLASSINDEX: TXT file with all Android API classes. Default: info/class_index.txt-C CLASSINDEX,--classIndex CLASSINDEX: TXT file with all Android API classes. Default: info/class_index.txt-SC SYSTEMCOMMANDSINDEX,--systemCommandsIndex SYSTEMCOMMANDSINDEX: TXT file with all System Commands. Default: info/system_commands.txt-C CLASSINDEX,--classIndex CLASSINDEX: TXT file with all Android API classes. Default: info/class_index.txt-mg MONGODBURI,--mongodbURI MONGODBURI: Exports the report generated to a mongodb database. Requires connection address following the scheme: localhost:27017-csv EXPORTCSV,--cexportCSV EXPORTCSV: Exports the report generated to a CSV file. Only static features are included.--color: Allow colors when printing messages.--no-color: Do not use colors to print messages.
MODE B - USING THE SOURCE CODE
NOTE: This procedure has only been tested in Ubuntu
0. Requirements
- AndroPyTool has a series of dependencies. You can install all of them by executing:
$ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends software-properties-common wget git lib32gcc1 lib32ncurses5 lib32stdc++6 lib32z1 libc6-i386 libgl1-mesa-dev python-pip python-dev gcc python-tk curl $ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/java -y $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo echo oracle-java8-installer shared/accepted-oracle-license-v1-1 select true | sudo /usr/bin/debconf-set-selections $ sudo apt-get install -y oracle-java8-installer $ sudo apt-get install -y python-setuptools $ sudo apt-get clean
1. You need to install Android SDK (go to next step if you already have it) The next steps will allow you to install Android SDK in Non-GUI mode:
- Download and unzip Android SDK:
$ cd $ wget http://dl.google.com/android/android-sdk_r24.2-linux.tgz $ tar -xvf android-sdk_r24.2-linux.tgz - Add Android SDK to path (if you don’t use Bash i.e. you prefer Zsh, remember to modify the correct file). To to that, add these two lines to your
~/.bashrcfile:export ANDROID_HOME=$HOME/android-sdk-linux/ export PATH=$PATH:$ANDROID_HOME/tools export PATH=$PATH:$ANDROID_HOME/platform-tools -
Load the libraries in the current session with:
$ source ~/.bashrc2. We have to install the Android 16 package
-
Let’s install Android 16, which is the version supported by DroidBox (the platform and system image):
$ echo y | android update sdk --filter platform-tools --no-ui --force -a $ echo y | android update sdk --filter tools --no-ui --force -a $ echo y | android update sdk --filter android-16 --no-ui --force -a $ echo y | android update sdk --filter sys-img-armeabi-v7a-android-16 --no-ui -a3. Let’s download the repositories
- Now we can download the AndroPyTool repository from GitHub. It has some dependencies which will be also downloaded. In the case of DroidBox, the last release of the original DroidBox repository is also downloaded in order to copy the system and RAM images:
$ git clone --recursive https://github.com/alexMyG/AndroPyTool.git $ wget https://github.com/alexMyG/AndroPyTool/releases/download/droidbox_images_patched/images_droidbox.zip $ unzip -o images_droidbox.zip -d AndroPyTool/DroidBox_AndroPyTool/images $ touch AndroPyTool/avclass/__init__.py
3. Let’s prepare DroidBox
- We need to give the necessary permissions to all the scripts
$ chmod 744 AndroPyTool/DroidBox_AndroPyTool/*.sh - Now we have to create the Android device:
$ echo "no" | AndroPyTool/DroidBox_AndroPyTool/createDroidBoxDevice.sh
4. Let’s install the Python libraries required
- This repo requires several Python libraries. We recommend you to use a Virtual Environment. If you do not want, go to next step:
Install
virtualenv:$ sudo pip install virtualenvCreate virtual environment and activate it:
$ virtualenv droidbox_env $ source droidbox_env/bin/activate - The following Python libraries are required:
$ pip install -r AndroPyTool/requirements.txt5. Now we can run AndroPyTool
- If everything was OK, we can now run AndroPyTool:
$ cd AndroPyTool/ $ python androPyTool.py -s </PATH/TO/FOLDER/WITH/APKS/> - See the arguments available above in the Docker section
Input and output folder structure
INPUT: A folder containing files with “.apk” extension. OUTPUT: A structure of folders following this scheme:
/ --> root folder
/samples/ --> samples, originally in the root folder
/samples/BW/ --> benignware samples
/samples/MW/ --> malware samples
/invalid_apks/ --> invalid apks found
/VT_analysis/ --> VirusTotal analysis reports
/FlowDroid_outputs/ --> flowdroid results
/FlowDroid_processed/ --> flowdroid results processed
/DroidBox_outputs/ --> DroidBox outputs raw
/Dynamic/Droidbox/ --> Droidbox analysis in JSON
/Dynamic/Strace/ --> Strace analysis in CSV
/Features_files/ --> Features files generated with AndroPyTool
Acknowledgements
- phamhduy fixed the Droidbox images.